
bernjuer/iStock/Getty Images
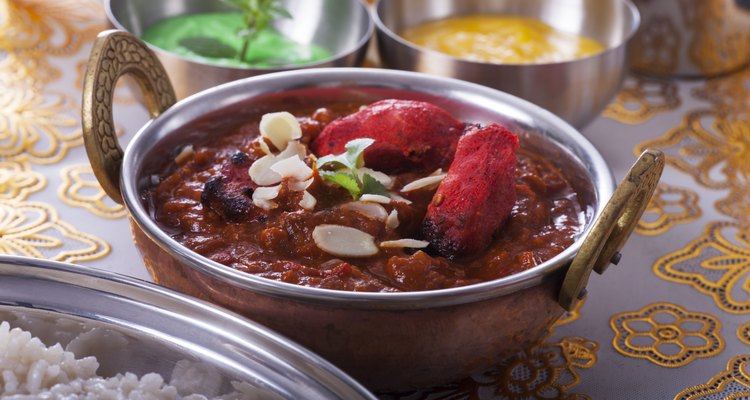
Indian cuisine, if prepared using low-fat cooking methods, can have many health benefits since many dishes contain legumes, vegetables and grains that are high in fiber as well as iron, according to the American Heart Association. Iron is needed in the body to carry oxygen from your lungs throughout our bodies as a part of the protein hemoglobin. According to the Centers for Disease Control, most individuals should consume 8 to 11 mg of iron daily, with more recommended for women of child-bearing age and those that are pregnant. The American Association of Physicians of Indian Origin, or AAPI, report that many Indian dishes are prepared from beans, meats and green vegetables and served with rice, all of which are rich sources of iron.
Dal
Dal refers to any legume as well as any complete dish or soup made with legumes. In Northern Indian cuisine, according to the AAPI, beans most frequently consumed include garbanzo, kidney, and urad. Such legumes, as well as lentils, contain about 2.5 to 3 mg of iron per 1/2 cup serving, according to the USDA Nutrient Database. Dal is usually served with basmati rice or a bread such as naan or whole grain chapati bread. Rice such as basmati contains about 2 mg of iron per cup.
Tandoori
Tandoori dishes are named for the tandoor, or clay oven in which the dish is cooked. Common tandoori dishes include chicken and lamb, both of which are popular meats in Indian cuisine. Such meats, according to the AAPI, are usually prepared with such spices as onion, ginger, and garlic, and served with basmati rice. One 3 oz. serving of chicken and lamb, according to the USDA Nutrient Database, contains between 1 and 2 mg of iron. Some meat dishes in Indian cuisine may also be garnished with nuts such as cashews, which contain about 1.7 mg of iron per ounce.
Other Sources of Iron in Indian Cuisine
Mixed dishes, such as curry, can contain many iron-rich foods such as meats, beans, as well as some vegetables. Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, contain about 3 mg of iron per 1/2 cup cooked, according to the USDA Nutrient Database. After dinner desserts in Indian cuisine may also be helpful to iron absorption. Plantains contain about 1 mg of iron per cup, while fruits such as mango, guava, and oranges contain vitamin C that help with absorption of iron. Those vegetarian sources of iron, such as beans, may not be as bioavailable as animal product sources of iron, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization, so vitamin C eaten around the same time as such foods aids with absorption of iron.
Related Articles

A List of Foods That Contain Choline

Foods Rich in Magnesium & Phosphorus

Which Is Healthier, Lima Beans or ...

Vitamin B2 for Hair Growth

The Nutrition of 15-Bean Soup

Foods High in Fiber and Iron

What Vitamins Help the Liver?

How to Iron a Uniform Shirt

Instructions for a Proctor Silex Iron

Calories per Cup of Cooked Navy Beans

Substitute for Gram or Besan Flour

L-Lysine for Hair Growth

How to Cook Pork Loin

Vitamins for Mental Alertness

Essential Enzymes for Hair Growth

Red Kidney Beans Nutrition

How to Use Panko
Southeast Asian Diet & Nutrition

How to Cook Quinoa Flakes for Breakfast

What Type of Food Do People in Honduras ...
References
Resources
Writer Bio
Originally from Maryland, Staci Gulbin started writing professionally in 2010. Her work has been published on a Baltimore news website as well as other online entities. Gulbin holds graduate degrees in biology and nutrition from New York University and Columbia University, and is a registered dietitian and certified personal trainer.
Photo Credits
bernjuer/iStock/Getty Images