
Preto_perola/iStock/Getty Images
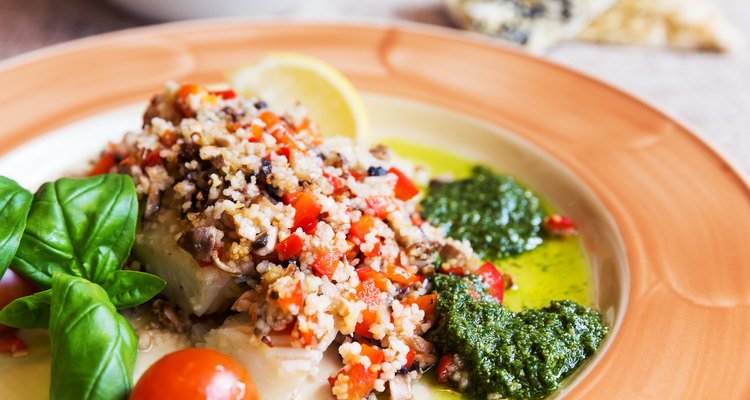
Consuming a healthy diet is the foundation of maintaining your overall physical and mental wellness. Poor dietary habits contribute to the development of the leading killers in America, including heart disease, cancer and diabetes. Numerous diet programs claim the best health benefits, yet conflicting information makes choosing the right nutritional path difficult. The Paleo and Mediterranean style diets are two similar programs emphasizing diet as a way of life, not a temporary solution. Each has benefits and clinically evidenced effectiveness for reducing risk of health complications. Choose what works best for you based on credible information and consultation with your physician.
Paleo Diet Basics
The Paleo diet is based on the concepts of eating foods off the land as the ancestral hunters and gatherers from the Paleolithic period once did. Before industrialization, technological advances and science assisted in farming, slaughtering and packaging foods, the ancient Paleolithic people hunted free range game, fished in seas that were not exposed to toxic dumping and gathered crops from pesticide free land. Emulating this form of diet in modern times is not as difficult as it may seem, and you are not expected to find wild game to hunt and build a farm in your back yard. The basics boil down to fruits and vegetables as the foundation, incorporating lean sources of protein from poultry or fish and obtaining healthy fats from nuts, seeds or grass-fed meat sources. Grains are not emphasized in this diet plan.
Mediterranean Diet Basics
The Mediterranean diet is modeled after the eating habits and cooking styles of people living in countries that border the Mediterranean Sea, including Greece and Italy. This diet emphasizes more daily servings of fruits, vegetables and grains than any other food group. Consuming fish at least twice a week and eating moderate portions of dairy and poultry are part of this diet. Lean meats are allowed, however, less is best. Light to moderate consumption of red wine with meals and use of olive oil are also important components of the Mediterranean diet.
Similarities and Differences
The Paleo and Mediterranean diets both make use of fish as optimal sources of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Limiting the amount of saturated fat in your diet is one crucial component of heart health, which each diet recognizes. Both diets encourage several servings of fruits and vegetables for getting the vitamins, nutrients and antioxidants required to maintain health and prevent disease. The diets also highlight eating nuts, seeds and use of olive oil for flavoring over fatty dressings and junk food snacking. The diets differ in the consumption of dairy foods and of grain products like breads, pastas and cereals. MayoClinic.com notes that the Mediterranean diet encourages eating low-fat dairy to maintain calcium, vitamin D and protein needs. Whole grains are equally important to provide fiber for healthy digestion and keeping cholesterol levels lower.
Benefits of Paleo-Mediterranean Dieting
According to a 2009 pilot study in "Cardiovascular Diabetology," diabetic participants placed on a Paleo diet showed improved blood sugar control and reduced risk for cardiovascular disorders compared to eating a diabetic diet alone. Similarly, the "British Medical Journal" published a 2008 study of non-diabetic participants on a Mediterranean style diet that had a 35 percent reduction in risk for developing diabetes due to changing eating patterns. The crux of choosing a Paleo or Mediterranean diet lies in limiting foods with saturated fats and refined sugars while also increasing consumption of raw produce that promotes arterial health and normal digestion. Both diets offer benefits for cardiovascular health, prevention or management of glucose-related disorders and a means for consuming foods that may protect against forms of cancer. Choose the right nutritional plan based on your current health status and recommendations from your physician.
Related Articles

Traditional English Diet

Mediterranean and Asian Diets

How to Make Your Own Lean Cuisine

Which Cooking Oil Can You Use on the ...
Southeast Asian Diet & Nutrition

Can You Eat Paddlefish?

What Is the Michi Ladder Diet?

High Fiber & Protein Diet Menus

Farm-to-Table Concept

Is All Chinese Food Fattening?

How to Bake Boneless Skinless Tilapia

Foods Containing DMAE

Traditional Hawaiian Diet

Can I Exercise on the Master Cleanse ...

Are Pickled Vegetables Allowed on a Raw ...

List of Vegetables for the Paleo Diet

What Is the Nutritional Value of an ...

Can Eating Salads & Fish Make You Lose ...
Meals With No Starch

The History of Asian Food
References
- MayoClinic.com: Mediterranean Diet
- "Cardiovascular Diabetology"; Beneficial Effects of a Paleolithic Diet on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Cross-Over Pilot Study; Tommy Jonsson et al; July 2009
- "British Medical Journal"; Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Developing Diabetes: Prospective Cohort Study; M. A. Martinez-Gonzalez et al; May 2008
- Women's Heart Foundation: The Mediterranean Diet
Resources
Writer Bio
Aubri John has been a contributing researcher and writer to online physical and mental health oriented journals since 2005. John publishes online health and fitness articles that coincide with her licensed clinical skills in addictions, psychology and medical care. She has a master's degree in clinical social work and a Ph.D. in health psychology.
Photo Credits
Preto_perola/iStock/Getty Images