
balticboy/iStock/Getty Images
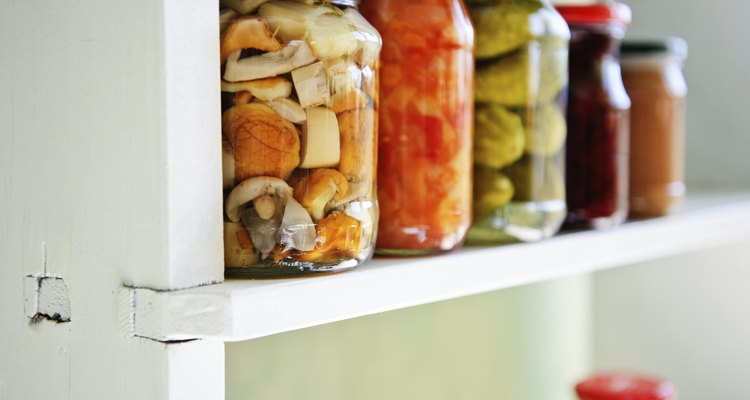
Based on the notion that raw foods are nutritionally superior to their cooked counterparts, the raw food diet embraces a variety of unheated foods such as fruit, vegetables, seeds and nuts. Although you can consume some forms of pickled vegetables and other fermented foods on this diet, varieties that have been boiled, pasteurized or otherwise heated are not considered acceptable on a strictly raw menu.
Description
According to the Oregon State University Extension, pickling is an ancient method of preserving food, which can prevent vegetables, fruit or other perishable items from spoiling. Pickles typically come in two forms: fermented, where vegetables cure in brine for several weeks, and unfermented, where vegetables sit in an acidic solution such as vinegar for one to two days. Although the word "pickle" typically evokes images of jarred cucumbers packed in brine, a spectrum of pickled vegetables are available, including varieties suitable for a raw food diet. Judith Choate, author of "The Best Little Book of Preserves and Pickles," states that virtually every vegetable can be pickled.
Heat Treatment
Nazlina Hussin, chef and author of Pickles and Spices World, explains that young, tender vegetables are pickled while still raw, while older vegetables are more likely to be cooked before pickling. Yet, even when vegetables are placed in brine in their raw form, additional processing steps may render them unacceptable for a raw food diet. The Oregon State University Extension indicates that pickles are typically processed with either a boiling-water method or a pasteurization method, both of which cause the pickles to exceed the 116 degrees Fahrenheit limit allowed on a raw food diet. Although most commercially sold pickles have been heated and aren't considered raw, some companies produce pickled vegetables that are cured and packaged at low temperatures. Such pickled vegetables, typically labeled "raw," "living" or "unpasteurized," are allowed on a raw food diet.
Benefits
Along with retaining the vitamins, minerals and fiber contained in fresh vegetables, raw pickles may offer additional health benefits. According to author Rebecca Wood, pickling can make vegetables more digestible, neutralize naturally occurring anti-nutrients, and replenish the gut flora needed for smooth digestion. Wood notes that the unpasteurized pickles eaten on a raw food diet are more healthful than pasteurized varieties, because the heating process destroys the helpful micro-flora that grow during the pickling and fermenting process.
Considerations
Although raw, pickled vegetables can offer valuable nutrition, they may also pose a risk of food-borne illness if not properly prepared. Although pasteurization destroys the friendly bacteria that can boost your intestinal health, heating also destroys harmful pathogens responsible for disease. In addition, while raw fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds can be a valuable component of your diet, a strictly raw food diet may lack critical nutrients and result in deficiencies over time. Consult your physician before embarking on a strictly raw eating plan.
Related Articles

The Advantages of Pickling Foods

How to Pickle Brine Sausage

How to Use Sea Salt for Canning

Can You Use Frozen Vegetables in a Raw ...

Difference Between Soba and Udon Noodles

Shelf Life of Frozen Foods

Hydroponic Vegetable Nutrients Vs. ...
Substitutes for Alum in Pickling

Are There Foods That Heal Age Spots?

How to Make Cucumber Kimchi
Uses of Saltpeter in Food

A List of Foods Containing Microbes

List of Foods That Are Commonly ...

The Difference Between Pickles & ...

Can You Make Pickled Lettuce?
How to Cook Fresh Sauerkraut and ...

What Are the Dangers of Sauerkraut?

How to Process Sauerkraut into Canning ...
How to Pickle Without Vinegar

What Are the Health Benefits of Pico De ...
References
Writer Bio
Denise Minger, an independent researcher, writer, editor and public speaker, published her first book, "Death by Food Pyramid," in January 2014. Passionate about health, she runs a blog at rawfoodsos.com dedicated to debunking bad nutritional science, and offers health consultations for individuals with special dietary goals.
Photo Credits
balticboy/iStock/Getty Images