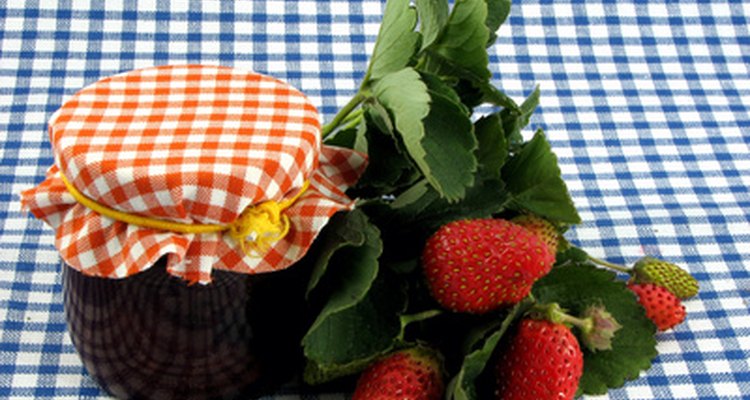

Homemade jelly is made by mixing and cooking fruit, sugar, acid and pectin. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the appearance, texture and taste of homemade jelly are dependent upon precise canning techniques. Furthermore, the ingredients must be mixed properly to achieve the most appetizing jelly.
Cooking Method
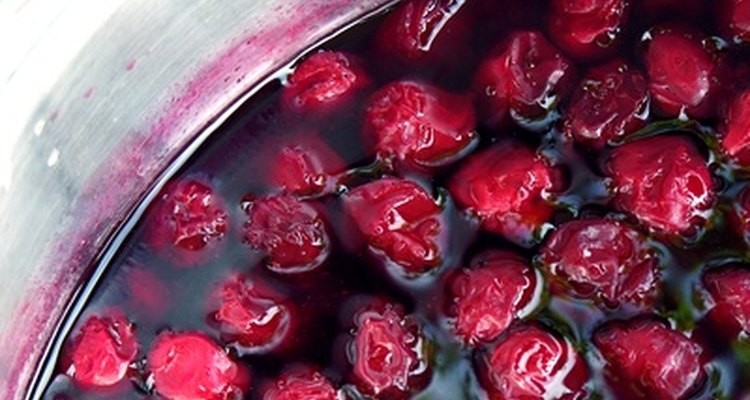

Cutting the cooking time short can cause visible sugar crystals in the jelly. In "The Art of Home Canning," Angelo Sorzio says to cook the jelly longer to avoid the formation of sugar crystals. The Oregon State University Extension Service directs cooks to boil the jelly rapidly and remove it from the heat as soon as it is done.
Type of Fruit
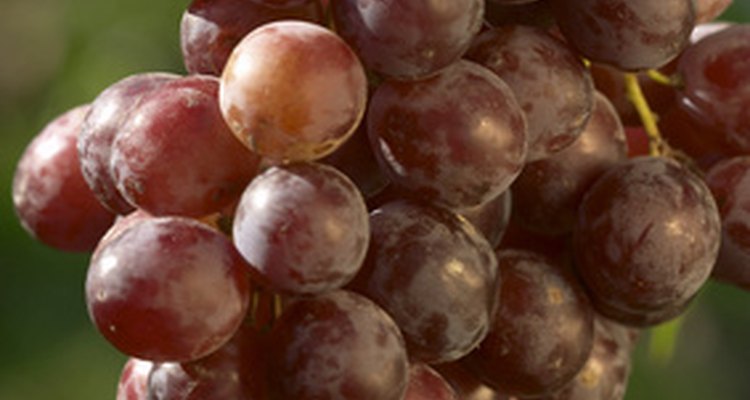

Crystals form in grape jelly because it naturally contains tartaric acid. Cooks can reprocess grape jelly for the same amount of time as originally processed to get rid of the crystals, Sorzio says.
Ingredients
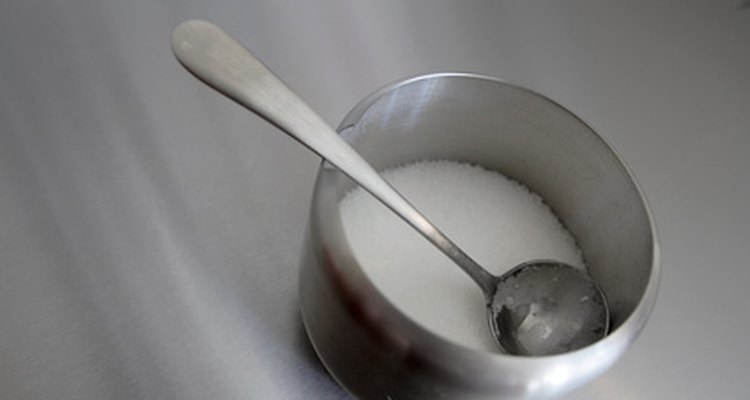

Too much sugar will leave glass-like particles throughout the jelly, Sorzio claims. Choose modern recipes for jelly and follow the instructions exactly to prevent sugar crystals from forming. The U.S. Department of Agriculture cautions that sugar should not be replaced with a substitute unless the recipe includes the correct amounts to use as a substitute.
Wrap-Up

Sorzio also suggests using a ladle to spoon any type of jelly into clean jars instead of pouring it in from the pan. This technique keeps sugar that does not dissolve from sweeping from the sides of the pan into the jelly. The jars should be hot when the jelly is added.
Related Articles

Why Do You Put Lemon Juice in Jelly?

Tayberry Jam Recipe

Baking With Juice Concentrates

How to Seal Jelly With Wax

How to Make Tomato Jelly

How to Make Sugar Wax?

How to Make Old Fashioned Apple Jelly

How to Make Whipped Frosting Without ...

How to Make Sugaring Wax

How to Dye Your Beard and Not Stain ...

How to Use Coke to Tenderize Pork

Candied Fruit for Baking

How to Make Blueberry Jam

How to Freeze Raspberries
How to Use Arrowroot to Thicken a Fruit ...

How to Use Honey to Remove Milia

How to Make a Lip Mask for Extremely ...

When Does Salami Spoil?

How to Melt White Sugar for Flan
How to Soften Plaque on Teeth
References
- "Complete Guide to Home Canning, Preserving and Freezing"; United States Department of Agriculture; 1994
- "The Art of Home Canning"; Angelo Sorzio; 1976
- Oregon State University Extension Service: Jams and Jellies Problems and Solutions
Resources
Writer Bio
Jenny Braswell began her professional writing career as a grant writer in 2005. Her articles have appeared in local newspapers and "Charm" magazine. She is a graduate of the Rural Economic Development Institute. Braswell received her Bachelor of Arts in international studies from Meredith College.
Photo Credits
jam image by dinostock from Fotolia.com