
dolgachov/iStock/Getty Images
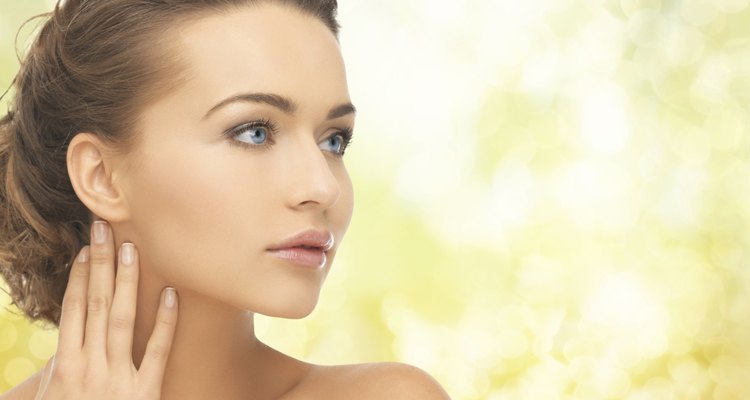
Glucosamine is a nutrient that is a natural component of healthy cartilage, according to the Mayo Clinic. Randomized controlled studies have shown the benefits of glucosamine for osteoarthritis, believed to be primarily due to its ability to strengthen cartilage. Glucosamine is also sometimes touted for its skin benefits, though there is little scientific evidence to back up many of the claims. Glucosamine is most often taken in supplement form, as it primarily is found in tissues and bones of animals that are not typically consumed.
Reduce Wrinkles
One of the big purported benefits of glucosamine for the skin is that it can help in the reduction of wrinkles. In her book "Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice," Dr. Leslie Baumann states that glucosamine has demonstrated various cutaneous benefits, including wrinkle reduction. She references a study of 53 women that found a 34 percent reduction in visible wrinkles after five weeks of taking a supplement that contained glucosamine and various antioxidant compounds.
Treat Hyperpigmentation
Another benefit of glucosamine for the skin is that it can help to treat hyperpigmentation, according to Baumann. Hyperpigmentation is a darkening of skin area due to an increase in melanin, usually due to sun damage, inflammation or acne. It can show up in large or small patches. The way glucosamine impacts hyperpigmentation is through inhibiting tyrosinase activation, which suppresses melanin synthesis, explains Baumann.
Wound Healing
Glucosamine also seems to support wound healing. In his book "100 Super Supplements for a Longer Life," nutritionist Frank Murray explains that the production of hyaluronic acid in the early stages of wound healing is of critical importance as it cements subcutaneous tissue. Taking glucosamine by mouth, especially directly after trauma to the skin, enhances hyaluronic acid production and promotes faster wound healing. If you suffer from getting wounded easily, this supplement may be helpful.
Moisturizing
Another benefit that glucosamine may provide is moisture for the skin. Paula Begoun states in her book "The Complete Beauty Bible: The Ultimate Guide to Smart Beauty" that glucosamine has value as a moisturizer since it is made up of mucopolysaccharides, long chains of amino sugars found in the body's tissues. Glucosamine is also a natural component of the skin's composition. You may have less of a need for an external moisturizer when you eat foods high in glucosamine, such as shellfish or meat that contains tissues, or supplement with the nutrient.
Related Articles

Alternatives to La Mer Creme

Seborrheic Dermatitis & Nutritional ...

The Best Anti-Cellulite Supplements
L-Arginine & the Skin

Amino Acids to Get Rid of Acne Scars & ...

Skin Care Products That Contain ...

How to Reduce Acne Inflammation

Home Remedies for Cellulite With Castor ...

Benefits of Shea Butter and Coconut Oil ...

The Best Vitamins for Sinuses

List of Retinoids

Collagen & Rosacea

How to Maintain Good Skin After Accutane

Oil of Olay & Wrinkles

Papaya & Acne
Bromelain & Bruising

What Is Palmitoyl Oligopeptide?

Benefits of Vitamin C for Facial Pores

What Are the Benefits of BioSil?

Can You Decrease Sebum With Vitamin A?
References
- "Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice"; Leslie Baumann, MD; 2009
- "100 Super Supplements for a Longer Life"; Frank Murray; 2000
- "The Complete Beauty Bible: The Ultimate Guide to Smart Beauty"; Paula Begoun; 2004
Writer Bio
Christine Garvin is a certified nutrition educator and holds a Master of Arts in holistic health education. She is co-editor of Brave New Traveler and founder/editor of Living Holistically... with a sense of humor. When she is not out traveling the world, she is busy writing, doing yoga and performing hip-hop and bhangra.
Photo Credits
dolgachov/iStock/Getty Images