
Kai_Wong/iStock/Getty Images
Raw food diets include meat products by default, unless they are combined with vegetarianism, which prohibits the consumption of meat and fish, or veganism, which prohibits the consumption of all animal products. For many people, the reason for becoming a raw vegetarian or a raw vegan is not that this is more healthy than adding raw lean meats and raw fatty fish to the diet but rather that eating animals or animal products is seen as unethical.
The Raw Diet
Raw diets prohibit cooking food. About 115 degree Fahrenheit is the maximum temperature that you can expose foods to, because enzymes and essential nutrients start to break down at higher temperatures. Raw dieters prepare foods in other ways besides warming them. Salting and pickling are acceptable raw food preparation methods. You can also use a blender to make delicious appetizers and side dishes, such as hummus, salsa and cold vegetable soups. Equipped with a dehydrator that blow-dries the food, your can make dried meat, raw crackers, cookies and bread substitutes.
Raw Meat and Fish
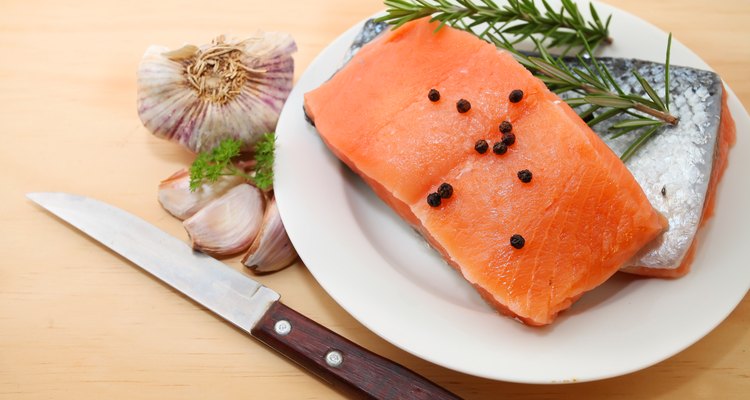
Eating raw meat and fish may initially seem unusual. However, many people regularly consume them. The fish component of sushi is raw, and carpaccio, a common appetizer at restaurants with a fusion cuisine, is raw meat pressed flat and spiced. Other ways to prepare raw meat and fish without cooking include salting, low-temperature smoking and marinating. Graved lachs is a common dish in Scandinavian countries. It is rather simple to make. Cut a boneless salmon fillet into two thin pieces, add 8 tsp. of salt and sprinkle with allspice. Place a large quantity of dill between the two pieces. Then put the two pieces together, wrap them in plastic wrap and add weight on top. Marinate it for 48 hours in the refrigerator. Empty any liquid and re-wrap half-way through. Rinse and cut off salty edges before eating it.
Health Risks of a Raw Food Diet With Meat
There are some precautions to take when dealing with raw meat. Raw meat can contain parasites, such as pin worms. Pin worms can live in the intestines and rectum of humans and can give rise to an itchy rectal area, especially at night when the female worms crawl out to lay eggs. Pin worms, however, are relatively harmless, and should you contract them, two treatments of a de-wormer from your local pharmacy can kill them completely. Raw meat and poultry may also contain bacteria, such as E. coli and salmonella, which can result in food poisoning. Food poisoning may require immediate medical attention. To minimize the risk of food poisoning, only purchase high quality, fresh meat.
Other Protein Sources
When eating a raw diet, not all of your protein needs to come from meat or other animal products. Legumes, such as black beans and chick peas, are good sources of protein. You cannot eat legumes raw. They are indigestible and may contain compounds that inhibit enzymes. Preparing legumes neutralizes these compounds and make the legumes more easily digestible. Sprouting is one way to prepare legumes on a raw diet. To sprout legumes, put them in a ventilated jar for one to five days. Keep them moist but not soaking wet throughout the process. Rinse the sprouting legumes frequently to prevent them from growing mold. Once sprouted, blend or combine them with minced vegetable, herbs and spices for delicious side dishes, dips or spreads.
Related Articles

African Food Facts

Rice & Lentil Diet

How to Make Dried Meat

Dangers of Spoiled Ground Beef

The Best Way to Smoke Yellowtail

How to Use Garbanzo Beans As a Meat ...

How to Soak Deer Meat in Baking Soda

How to Dry Meat With Salt

How to Make Chicken Noodle Soup Without ...

How to Cook Pork Loin

How to Salt Cure Jerky

How to Cook a Bullhead Fish

How to Cook Beef Topside in a Slow ...

How to Slice a Roast for Jerky

How to Slice Round Steak for Jerky

How to Cook Pancetta
Uses of Saltpeter in Food

How to Feed a Large Family Healthy ...

How to Make a Venison Rub

How to Make Venison Bratwurst
References
Writer Bio
Dr. Berit Brogaard has written since 1999 for publications such as "Journal of Biological Chemistry," "Journal of Medicine and Philosophy" and "Biology and Philosophy." In her academic research, she specializes in brain disorders, brain intervention and emotional regulation. She has a Master of Science in neuroscience from University of Copenhagen and a Ph.D. in philosophy from State University of New York at Buffalo.
Photo Credits
Kai_Wong/iStock/Getty Images