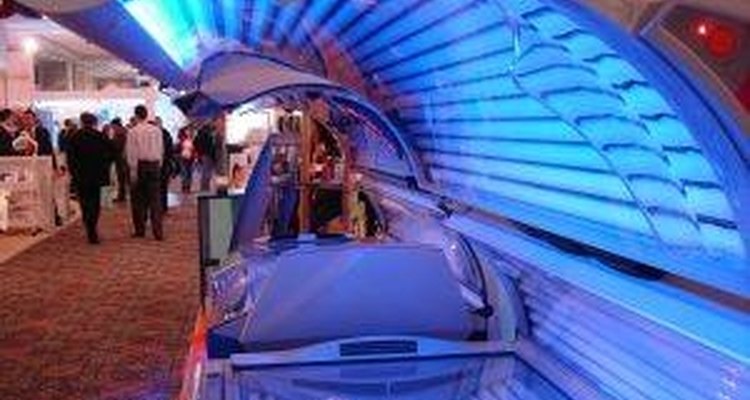

How Does a Tanning Bed Work?
Tanning beds, like the sun, emit ultraviolent (UV) radiation. Of the three types of UV rays, two are found in tanning beds--UVA and UVB-- and transmitted via several light bulbs. Typically, these bulbs emit about 95 percent UVA rays and 5 percent UVB rays, both of which are needed to produce a golden tan. UVA rays are the deepest penetrating form of UV radiation. Whereas UVB rays only penetrate the skin's top layer, UVA rays go all the way to the base layer of the skin. The combination of these rays create artificial sunlight that then stimulates melanin, which is the pigment that causes your skin to darken, and creates a golden tan. In natural sunlight, UVA rays are more abundant than UVB rays and are not affected by weather or altitude, so even if the sky is overcast or the weather is cold, UVA rays are still present. UVB rays, on the other hand, vary based upon the season, time of day and location, so they're not always reaching us. Although UVA rays are less likely to burn your skin, because they penetrate so deeply, many scientists believe they are responsible for premature aging of the skin.
From an electrical standpoint, tanning beds have fluorescent lamps inside them. A typical tanning bed consists of 10-50 lamps; each of these lamps uses between 100 and 200 watts of electricity. Unlike your everyday light bulb, tanning bed bulbs do not regulate the amount of electricity that flows through them. As a result, each bulb contains a small inductor (called a choke ballast) that limits the amount of current passing through. In simple terms, this means that the lamps will use the least amount of wattage that is needed to work effectively. Once the lamps are on, a combination of UVA and UVB rays are emitted as the tanner lies on the acrylic surface of the bed.
To further reduce burning, most salons now offer high pressure tanning beds. Unlike regular low pressure tanning beds, high pressure beds do not emit UVB rays, using only UVA rays instead. The bulbs used in high pressure beds are made out of quartz, which creates a high air pressure inside. This increased pressure then allows the bulbs to filter out all of the UVB rays. By using only UVA rays, a high pressure tanning bed is able to produce a darker tan more quickly.
While tanning beds do not transmit as much UV radiation as the sun, repeated exposure may still lead to skin damage. There is much debate regarding whether sunless tanning from tanning beds is safer than actual sunlight.
Related Articles

Uva Vs. Uvb Tanning Beds

Why Is UV Light Bad for Your Skin?

The Levels of Tanning Beds
Phototherapy Vs. Tanning Bed

How Does Ultraviolet Light Affect ...

How do Solar Watches Work?

UV Tanning Vs. Spray Tanning

Levels of Polarized Sunglasses

Example of Passive Solar Energy

Appliances That Use Solar Energy

How Does Infrared Cooking Work?

How to Start a Base Tan for Very Fair ...

Can You Wear Contacts While Tanning?

How Do Citizen Eco-Drive Watches Work?

How to Get a Natural Tan Fast

The Quickest Way to Get a Tan Without ...

Does Fire Roasting a Jalapeno Make It ...

Can LED Light Get Rid of Brown Spots on ...

How to Turn on a Tanning Bed at Tantopia

Tanning Beds and Eye Disorders
Writer Bio
Jessica Saras is a professional editor and copywriter. After earning an English degree from Reinhardt College, Saras completed the summer writing program at Sarah Lawrence College. A natural-born writer, she has more than six years of experience in web content development. In addition to being a full-time copywriter, she writes articles for Demand Studios, wiseGEEK.com, Examiner.com, and Suite101.com.
Photo Credits
Adem Kaya