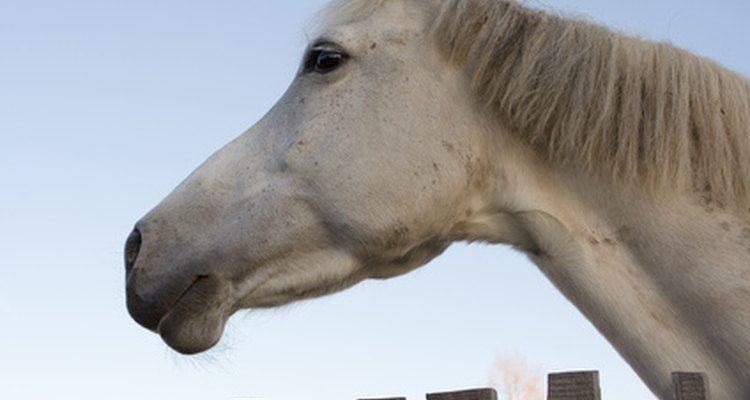

Lymph nodes are small round masses of immune tissue located throughout a horse's body that help protect it from infection and disease. Linked by lymph ducts throughout the body, they remove antigens from lymph fluid. Swollen lymph nodes may be a symptom of illness.
Clinical Significance
A wide range of conditions, from trivial to life-threatening, can cause swollen lymph nodes. Note the locations of the swollen lymph nodes, take your horse's temperature and observe any other abnormal symptoms. Call your veterinarian to determine the appropriate treatment.
Strangles Awareness
Swollen lymph nodes under the jaw and along your horses throat latch could point toward a disease known as strangles. Strangles is an infectious, contagious upper respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi equi. Symptoms include swollen or abscessed submandibular lymph nodes, fever, nasal discharge, cough and depression. Call your veterinarian immediately if your horse exhibits any of these symptoms.
Prevention/Solution
Because the causes of swollen lymph nodes are various, there is no single solution or prevention. As always, keeping your horse's environment clean, vaccinations current and limiting your horse's exposure to stress is your best line of defense against disease.
Related Articles

How to Train a Tarantula
How to Shave Skin Moles

Symptoms of Food Poisoning With Oysters

Problems With Nose Piercings

What Is the Function of the Amniotic ...

How to Heal an Inflamed Bikini Area

Initial Cleansing Effects of Coconut Oil

How to Get Rid of Stomach Hair ...

Copper Peptides Side Effects

How to Treat an Ingrown Eyebrow Hair

How to Cook Escolar Fish

How to Tighten Loose Ligaments

Metamucil Dosage for Cats

Can Borage Oil Help Acne?

How to Repair Open Pores

Are There Ways to Get Rid of Blocked ...

What Are the Causes of Hair Shedding in ...

Snail Cream Benefits

Chasteberry for Acne

How to Get Rid of a Dark Line Above My ...
References
Writer Bio
Gia Turner has been a writer since 2003. She writes freelance articles from her small working farm in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. When not writing, she cares for and trains horses, dogs and other domestic animals. Turner has contributed to ScienceBlogs.com and written for the Broward Psychological Association. She holds a Bachelor of Arts in psychology from Florida Atlantic University.
Photo Credits
horse image by Podfoto from Fotolia.com