
AmmentorpDK/iStock/Getty Images
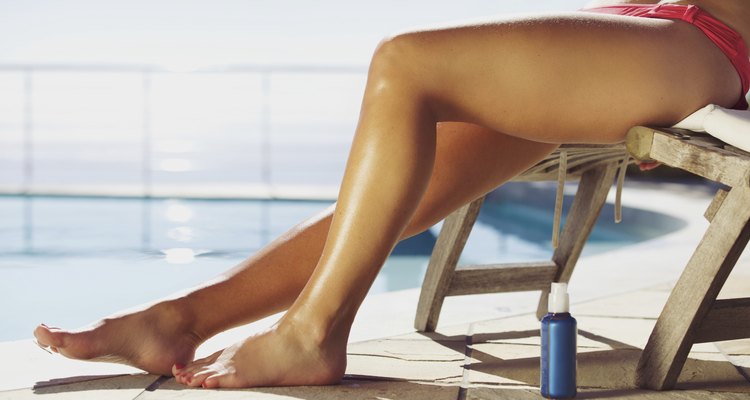
A spray-on tan can boost spirits during the long, cold winter and give a sun-kissed glow to anyone. Tanning sprays are just one of a variety of sunless tanning products that temporarily darken the skin without the need to spend time in the sun. As with any product to be applied to the skin, consider the risk of irritation before administering a spray-on tan. The pros and cons of using a tanning spray will depend in part on the lifestyle of each individual: convenience and cost versus health risks and appearance.
Lack of UV Rays
A clear pro when considering spray-on tans is that the artificial colorant does not cause damage to the skin as UV rays from the sun can. The chemical in tanning sprays is called DHA (dihydroxyacetone) and is approved by the FDA as a safe product to apply to the skin. People who use sprays at home should take care not to breathe in the fumes; CNN Health reports that the effects of accidental ingestion or inhalation of DHA is not clear. Spray-on tans do not protect the user from the sun's rays; protection in the way of sunscreen, hats and sunglasses is still important even when using sunless tanning products.
Even Coverage
Spray-on tans provide even coverage, which looks much more natural than an angry red sunburn on the shoulders and across the nose. Sunless tanning lotions and creams may be difficult to regulate in order to get an even coverage across the body, but sprays can be easier to manage, especially if a professional administers the tan in a salon or spa setting. The deeper skin hue does not appear immediately. Most people notice results within 24 hours of receiving their treatment.
Stains from Spray
Tanning sprays can stain clothing as well as skin, making it a potentially messy way to give skin a healthy glow. According to the CNN Health website, those who use sprays at home must wash off the product very quickly to avoid stains on their hands and under fingernails; the same is most likely true for wayward spray that comes in contact with the sink, mirror or other areas of the bathroom during the application process. Spray-on tans generally dry in about 15 minutes, which can be a plus when compared to other sunless tanning products like lotions and gels.
Short-Term Results
One of the disadvantages of a spray-on tan is that the color lasts for only a few days. The National Institutes of Health's service "UptoDate" explains that the colorant, DHA, fades within a week in most people as dead skin cells are shed. This can translate into an expensive venture for a prolonged tanned look. Sunless tanning sprays are available for purchase at most drugstores; self-administration of a spray-on tan may be less expensive than investing in numerous appointments at the local tanning salon.
Related Articles

UV Tanning Vs. Spray Tanning

The Best Way to Get a Tan If You Are a ...

How to Make a Spray Tan Last
How to Get a Good Tan From a Sun Lamp

How to Remove an Eyebrow Tattoo

How to Get a Base Tan in a Tanning Bed

How to Even Your Tan

Help With Chapped Red Cheeks

Sunbed Pros & Cons

How to Protect a Tattoo From the Sun

How to Fix Tan Lines on the Face

The Best Facial Moisturizers for People ...

Tips on Getting Spray Tans If You're ...

Dangers of Spray on Tan

How to Make Temporary Tattoos Last ...

How to Make Your Mystic Tan Last Longer

How to Prevent Pock Holes From ...

Can You Get a Spray Tan After Being ...

What Is the Difference Between Oily & ...

How Long After a Tattoo Can I Put ...
References
Writer Bio
Erica Roth has been a writer since 2007. She is a member of the Society of Professional Journalists and was a college reference librarian for eight years. Roth earned a Bachelor of Arts in French literature from Brandeis University and Master of Library Science from Simmons College Graduate School of Library and Information Science. Her articles appear on various websites.
Photo Credits
AmmentorpDK/iStock/Getty Images