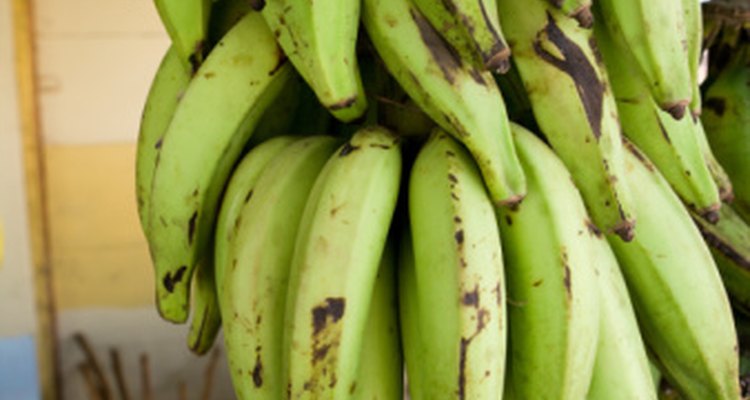

Plantains are from the same botanical family as bananas and appear almost identical. However, plantains are a starchy, low-sugar fruit and are used and consumed more like a potato than their sweeter cousin. The outer skin is very thick and difficult to peel when the fruit is unripe. Plantains are eaten around the world but are most popular in Latin America and West Africa, where they are a dietary staple.
Origins and Characteristics
Plantains originated in India and today are harvested in tropical areas around the world, as far north as California while South Africa provides the southernmost agreeable climate. The crop can be harvested year-round and a healthy and well maintained plant can produce fruit for nearly 50 years. It is believed that the plant was introduced to the west by Portuguese sailors in the 15th century and taken to the Americas by Spanish explorers in the 1560s. Plantains look identical to green bananas in appearance before maturing. When ripe, the outer skin is a dark brown or black. The plantain has a distinct different taste at each stage of development: similar to a potato or squash when green or yellow and more like a sweet potato or banana when brown or black. While the fruit grows sweeter as it ripens, plantains still possess a more bland and savory character than the saccharine traits of a banana.
Flavor Versatility
Plantains are most often consumed when they are starchy, under-ripe and green in color or when over-ripe, sweeter and the skin turns black. Because of the firm makeup of the fruit, plantains hold together much better than bananas. This factor, coupled with the relatively bland flavor, has resulted in plantains being served baked, boiled or fried on their own or as an ingredient in another dish prior to reaching the ripened stage. The fruit has been referred to by culinary experts as the pasta and potatoes of the Caribbean for its versatility and consistency as a starch in everyday meals. A popular way to prepare unripe plantains throughout the Caribbean and South America is to cut the fruit into thin slices and deep fry to create chips. When plantains attain their most ripe stage, they are often eaten in dessert dishes or fed to children as a sweet, healthy treat.
Health Benefits
The nutritional benefits of plantains make them a healthy choice in a balanced diet. An average-size plantain has about 220 calories and is a great source of vitamins C and A, as well as fiber and carbohydrates. Potassium rich, plantains help to maintain heart health and also are a great source of complex carbohydrates. which help sustain consistent energy levels.
One of a Kind
Because of their unique characteristics, plantains are an extremely adaptable food and are the rare fruit that can be served both savory and sweet depending on ripeness. Because of this, it is not a surprise that plantains have become so popular in the regions they are grown. Whether prepared as a sweet snack or as deep-fried chips, plantains provide a distinctive and nutritious addition to any diet.
Related Articles

List of Tropical Fruits

Types of Greek Fruits & Vegetables

How to Cook Plantains by Grilling & ...

Uses of Cassava Flour
What Fruits Have Edible Peelings?

Beans Vs. Lentils

Difference Between Soba and Udon Noodles

Can You Eat Celery Root Without Cooking ...

How to Make Melon Ice Cream
Southeast Asian Diet & Nutrition

What Kinds of Nuts Don't Grow on Trees?

What Type of Sugar Is in Fruit?

Can You Eat Frozen Edamame From the ...

Different Names for an Eggplant

The History of Butternut Squash

How to Clean Eggplant

How to Cook Plantains So You Don't Have ...

How to Cook Strawberries

Foods From Rainforest Plants

Green Bean Nutrition
References
Writer Bio
Jack Forbes has been writing sports, business and promotional material since 2000. His work was instrumental in two local political campaigns and the re-branding of a vacation home management company. His work has been featured in "The West Orange Times" and everythingpittsburgh.com. Forbes holds a Bachelor of Arts in history from Rollins College.
Photo Credits
Jupiterimages/Photos.com/Getty Images